ONS Consumer Prices Index September 2019
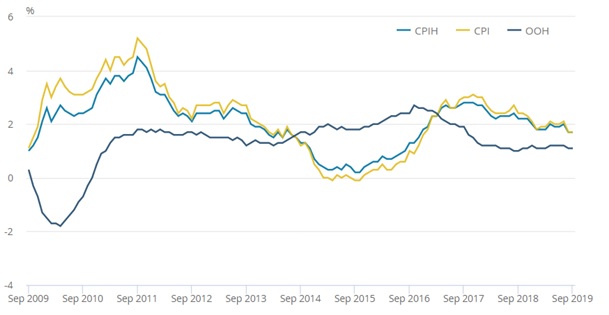
The headline Consumer Prices Index (CPI) rose 1.7%, year-on-year, in September, unchanged from the previous month. This was below expectations of a rise to 1.8% and below the Bank of England’s target.
The Consumer Prices Index including owner occupiers’ housing costs (CPIH) 12-month inflation also remained at 1.7% in September.
Downward contributions came from motor fuels and second-hand cars while furniture, household appliances and accommodation services exerted upward pressure.
Meanwhile, the Retail Price Index (RPI) and RPI (excluding mortgage payments, RPIX) slowed faster than expected, falling to 2.4%.
Pressure in the supply chain continued to ease in September with the Input Producer Price Index accelerating further into negative territory. Indeed, input price inflation now stands at -2.8%, the sharpest decline since May 2016. Crude oil was the main downward contributor, with annual price growth falling to -14.6%. Output inflation (factory gate) also weakened, falling to 1.2% year-on-year, from the 1.7% rise in the previous month and the lowest rate for three years.
The rise in some of the ‘non-core’ categories within the CPI measure resulted in core inflation (which excludes food and energy prices) rising to 1.7%, year-on-year, in September, up from the 1.5% rise in the previous month.
CPIH, OOH (owner occupiers’ housing costs) and CPI 12-month inflation rate for the last 10 years: September 2009 to September 2019
Source: ONS
Back to Retail Economic News